MMF is an ordinary choice to get 10 Gigabits per second speed above distances that data center and LAN enterprise applications require. We have several types of MMF available for excessive-speed networking installations and everyone with individual data-rate capacity and reach. Choosing the most appropriate multimode fiber with various options may be challenging. Which one should you select among OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5? This article can give you the answer.

How to Define Multimode Fiber?
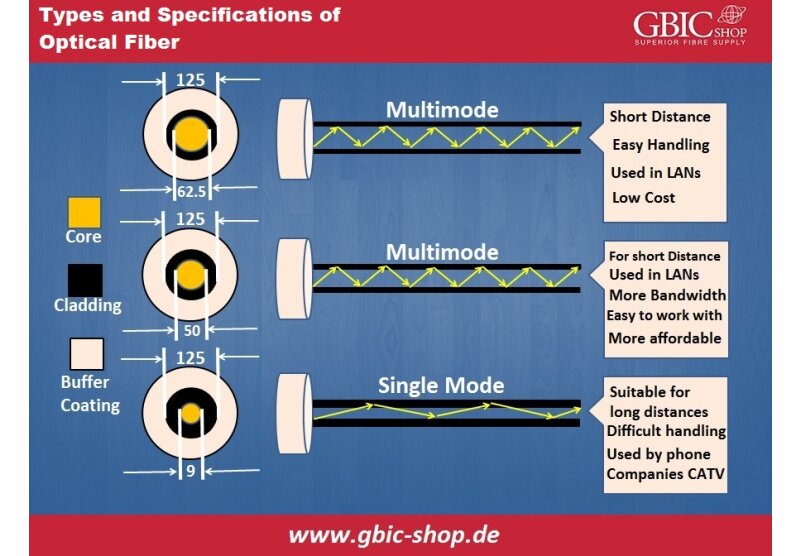
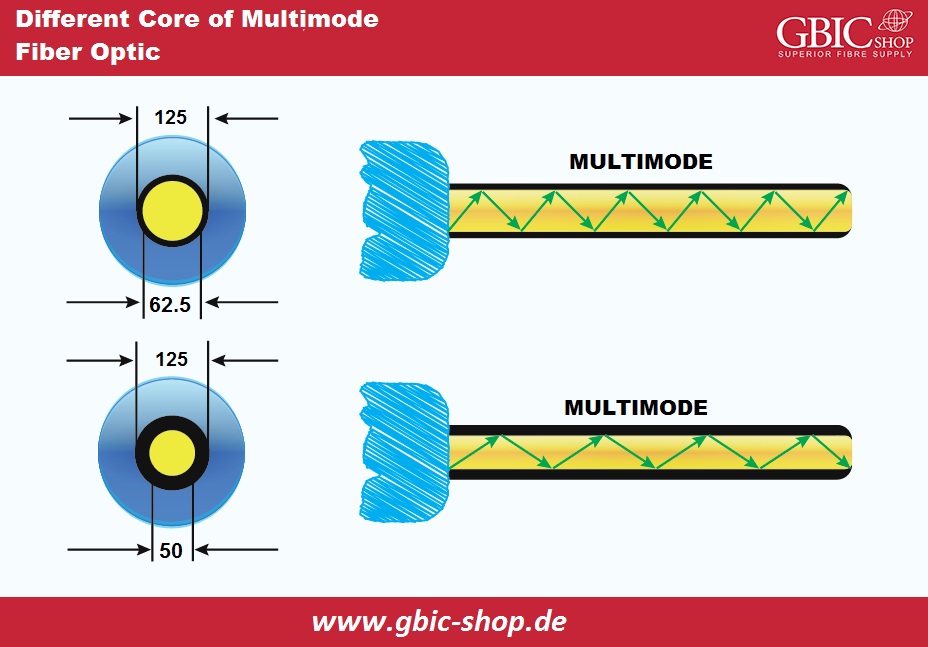
MMF is an optical fiber we mostly use in communication above short ranges. For example, for a campus or within a building. Multimode optical fiber cable possesses a great core, usually 50 and 62.5 microns, to propagate the different light modes. Due to this, additional data can get through the MMF core within a specific time. The highest communication distance for multimode optical fiber cable is about 550 meters at 10 Git/s speed. It can transfer farther at low data rates, like going around 2 kilometers at 100 megabits per second.
Types of Multimode Fiber:
As standard ISO 1180 identifies, we can classify MMF optic cables into OM1 Optical Fiber, OM2 optical fiber, OM3 optical fiber, OM4 optical fiber and the modern OM5 optical fiber. The following part will analyze these fiber optics from the angle of bandwidth, core size, distance, data rate, optical source, and color in detail.
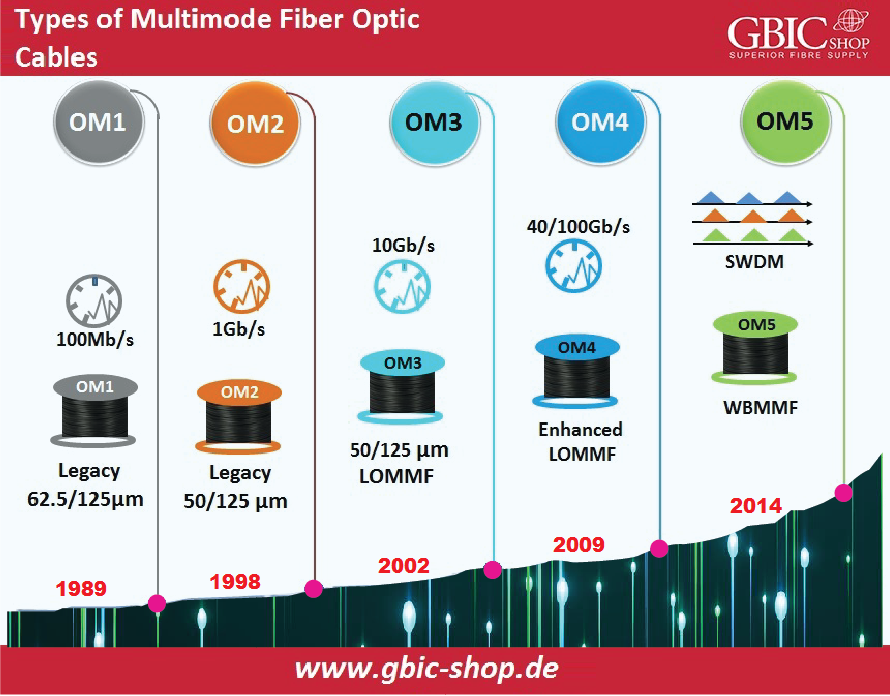
OM1 Optical Fiber:
OM1 optical Fiber has a 62.5 µm core size, and the color of its jacket is orange. It supports 10GbE at 33m lengths. We mainly use it for 100Mbps Ethernet implementations. This type typically utilizes a light source of LED.
OM2 Optical Fiber:
The color of the OM2 fiber jacket is also orange, and it possesses a 50 µm core size. It can support 10GbE at 82m lengths, but we commonly use it for 1GbE implementations. It utilizes a light source of LED.
OM3 Optical Fiber:
The color of the OM3 fiber jacket is aqua, and it possesses a 50 µm core size, but we have optimized the cable for laser-based equipment. This type of fiber supports 10GbE at 300m lengths. However, we commonly use 10GbE. Nevertheless, OM3 can help 40G and 10GbE to 100m.
OM4 Optical Fiber:
This fiber is backward adaptable to OM3 optical fiber and possesses a similar aqua jacket. We have developed OM4 specifically for laser transmission of VCSEL, enabling 10 Git/s connection ranges to 550 meters, contrary to 300 meters with OM3. Moreover, it can extend from 40/100GB to 150m using an MPO connector.
OM5 Optical Fiber:
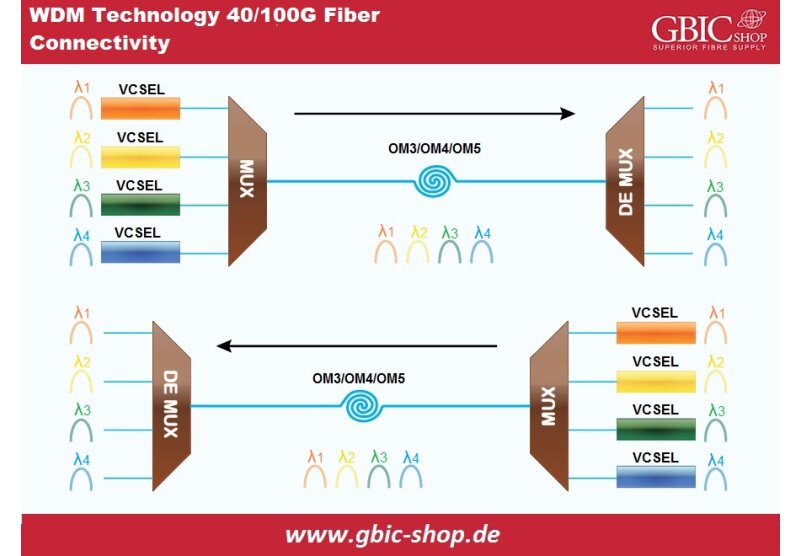
We can also signify this type of fiber as wideband MMF (WB MMF). OM5 is the modern type of MMF and is backward adaptable to OM4. It possesses a similar core size to OM4, OM3, and OM2. OM5 fiber's jacket color is lime green. We have designed and specified it to support four channels of WDM at 25Gbps speed per channel via 850-950 nanometers window.
Differences between OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5:
The main difference between multimode optical fibers lies in physical contrasts. Therefore, physical difference causes different communication data rate and range. Watch this video to understand the distinctions between OM1 fiber, OM2 fiber, OM3 fiber, OM4 fiber, and OM5 fiber.
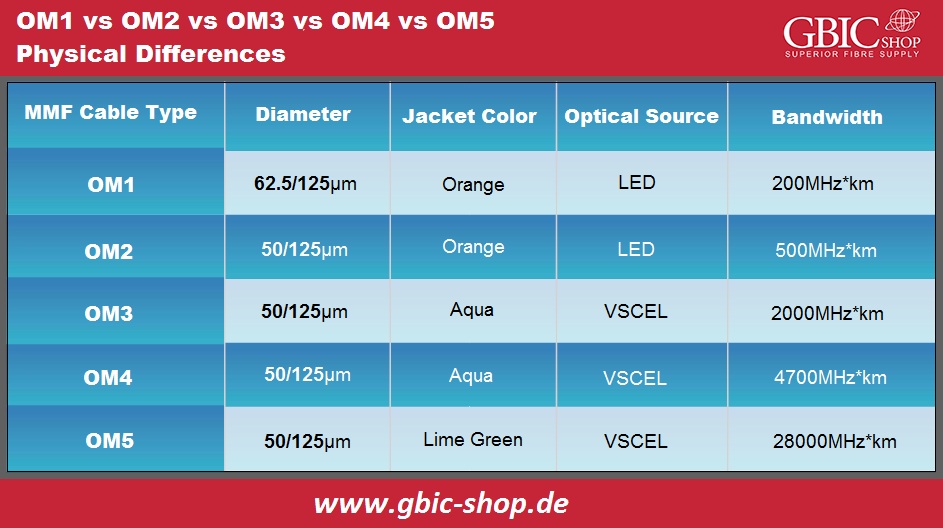
Physical Distinction:
The physical difference mainly rests upon jacket color, diameter, bandwidth, and optical source, which we have described in the table below.
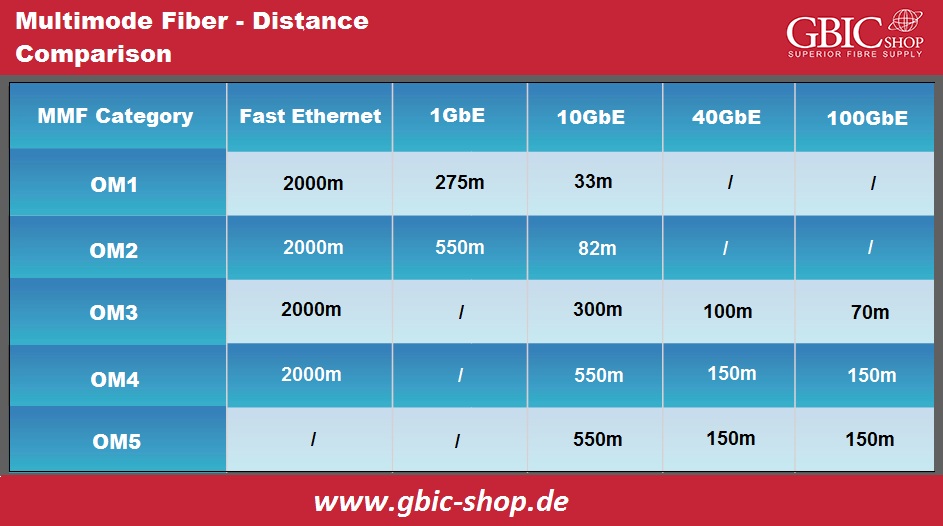
Practical Distinction:
Multimode fibers can transfer different distances at different data rates, and you can select the most appropriate one regarding your valid application. Below, we have specified the max MMF distance contradiction at a particular data rate.
Differences between Multimode and Single-mode Fiber:
Technical Distinction:
Core Diameter---SMF possesses a tiny 8 to 10,5 µm core that enables only one light mode to propagate. MMF contains a large 50 to 62,5 µm core allowing multiple light modes to reproduce.
Light Source---MMF devices typically use laser or LED sources of light. SMF devices use a laser diode or laser to create light.
Practical Difference:
Distance---Light proceeds through a long-distance within SMF cable compared to multimode cable. Therefore, MMF is appropriate for brief applications enabling transmission ranges to around 550 meters at 10 Git/s. We prefer SMF when the length is above 550 meters. Price---MMF is more cost-effective than SMF. Bandwidth---Single-mode's bandwidth is high compared to multimode, nearly 100,000 Gigahertz.
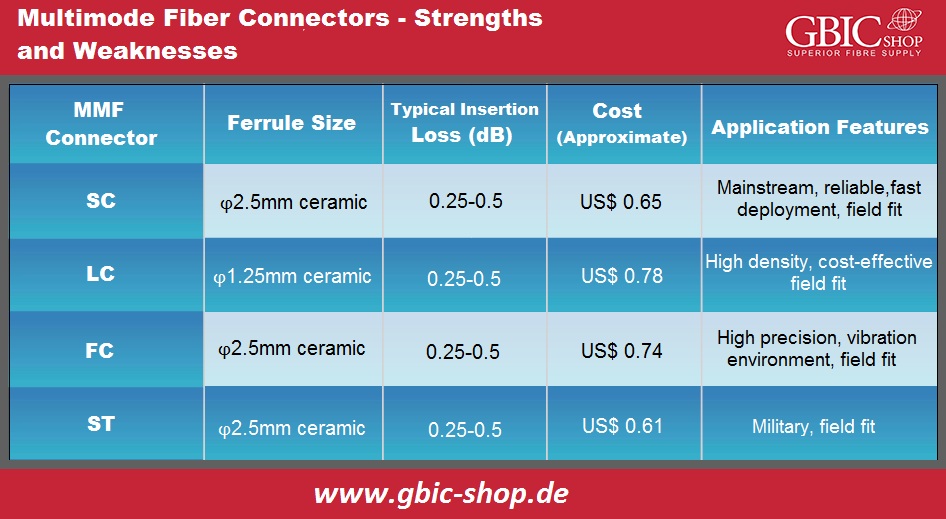
Types of Multimode Optical Fiber Connectors:
We have many MMF connectors in circulation like SC, ST, MU, FC, LC, E2000, SMA, DIN, MTRJ, MPO/MTP, etc. The optical fiber connector types which we most commonly use are SC, FC, LC, and ST. Each one possesses its benefits, capabilities, and drawbacks. Therefore, how can we differentiate them? The table below consists of standard MMF connectors and analyzes weaknesses and strengths.
Benefits of Multimode Optical Fiber:
Although SMF patch wire is superior regarding bandwidth and range for extensive distances, MMF effectively supports most lengths that we require for data center and enterprise networks at a price dramatically low compared to SMF. Nevertheless, MMF cable still possesses many significant benefits.
Multiple User Structure without any Interference:
MMF presents carrying different signals in a similar line simultaneously. Significantly, the total strength within the signs holds no loss. So, the network consumer can convey more packets within the cable simultaneously, and delivering information to the destination is possible without interference.
Support of Different Protocols:
MMF can support various data transmission protocols incorporating Internet protocol, Ethernet, and InfiniBand. So, one can utilize the wire as the key to a sequence of popular applications.
Inexpensive:
MMF and basics are cost-effective with excellent alignment tolerances and an extensive fiber core. They are uncomplicated to operate with other fiber optic components such as fiber adapters and fiber connectors. Moreover, multimode patch cables are inexpensive to install, work, and maintain compared to SMF cables.
Conclusion:
Generally, MMF cable is an inexpensive choice for data center and enterprise applications in the 500-600m range. Because of its reliability and high capacity, we usually use multimode fiber for backbone implementations in buildings. However, we cannot substitute SMF cable with MMF. As for what to select, a multimode fiber optic patch cord or an SMF patch cable. It all relies on the implementations you require, covering transmission distance and allowance of the total budget.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol