Hyper-scale companies are developing 200/400/800 Gigabit networks, whereas some others are still operating to migrate to 100 Gigabit networks. 40/100 Gigabit cabling solutions are similar in fiber and interface selection. Still, each implementation will depend on various factors like data throughput, cost budget, the infrastructure of the data center, and so on. The 40/100 Gigabit MMF solution within a data center can recognize the reasonable wiring plan through various technical procedures.
Recommendations for Upgrading 40/100G Networks:
Internet’s fast development and the modernization of 40/100 Gigabit data centers have led to changes and improvements in the cabling and internal infrastructure of data centers. An example is the deployment of various 40/100 Gigabit multi-mode fiber optic cables. Here are some factors that affect data centers’ upgrades.
Communication Distance and Amount of Loss:
The cable length is short for leading data centers, and the connection loss due to its transmission range is slight. Moreover, the connection power loss is comparatively significant. As the number of connections to data centers grows, so makes the power loss. So, data center wiring must strike a balance between performance and manageability. Selecting low-loss 40/100G MMF or utilizing SWDM technology effectively ensures the cabling environment in the data center.
Cable Infrastructure Design:
TIA-942, a telecommunication infrastructure standard for data centers, has focused on wired infrastructure environments. A structured cabling system that we founded upon 40/100 Gigabit MMF can expand or move according to the needs of the data center and throughput requirements change. A structured wiring system can decrease electricity costs by reducing overhead and under-floor cables and airflow resistance. Structured cabling solutions also support modular design, allowing maintenance or upgrades by replacing just the connectors without eliminating the horizontal wires or splitters.
Connectivity Options of 40/100 Gigabit Cabling:
While developing 40/100 Gigabit cabling, we have various connectivity choices to consider.
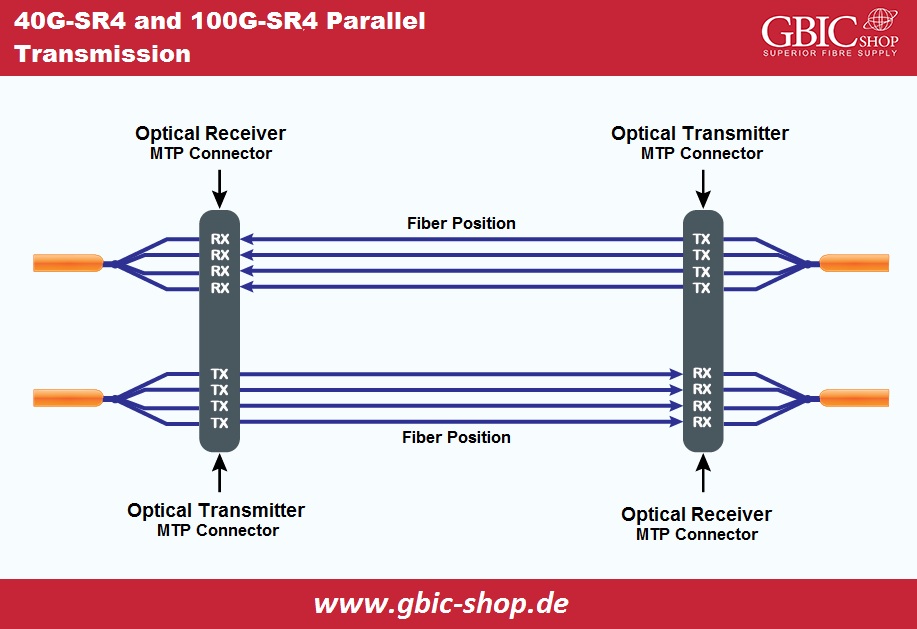
Short-distance multi-mode optical transmission module primarily refers to parallel transmission by combining multiple optical fibers to transmit and receive data. The 40/100 Gigabit multi-mode fiber optic cables can use the SR4 40/100 Gigabit optical module for data communication. With upgrading to 802.3bm, 100 Gigabit SR4 supports 100GbE speed using 12 optical fibers with multi-fiber push-on interfaces.
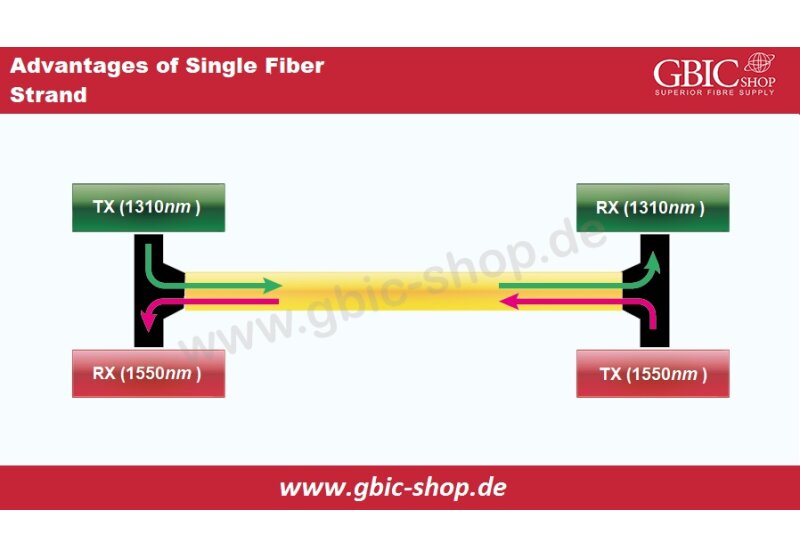
The QSFP-MM fiber optic module provides an MPO interface with more choices. LC duplex packaging has many advantages in terms of performance, cost, etc. In 40G QSFP and bi-directional SFP transceivers, we can use the LC duplex packaging to boost data communication performance.
Connectivity Solutions of 40/100 Gigabit Multi-mode fiber:
Datacenter speeds have increased from 10 Gigabit to 40/100 Gigabit, and deployment of 100m OM3/OM4 links is becoming commonplace. However, we have two specific data center deployment methods, each of which can realize 40/100 Gigabit multi-mode optical data communication within a data center.
Parallel Optical Transmission:
Parallel fiber optic technology allows data transference and reception through different fiber optics and is valuable for reliable and cost-effective cable designs. For instance, 40GBASE-SR4 parallel needs four OM3/OM4 in receiver and transmitter, each with a 10G data rate to accomplish 40 Gigabit transmission.
In 100 Gigabit multi-mode optical channels, OM3/OM4 transmission range is up to 300/400m. Similarly, 100GBASE-SR4 transmitters and receivers must use ten OM3/OM4 optical fibers to transmit. However, VCSEL technology's development has increased the accessibility of 25 Gigabit modulation rates, allowing duplex MMF of the MTP/MPO interface to attain the characteristics of using four fibers for reception and transmission, thereby reducing the loss in the optical connection.
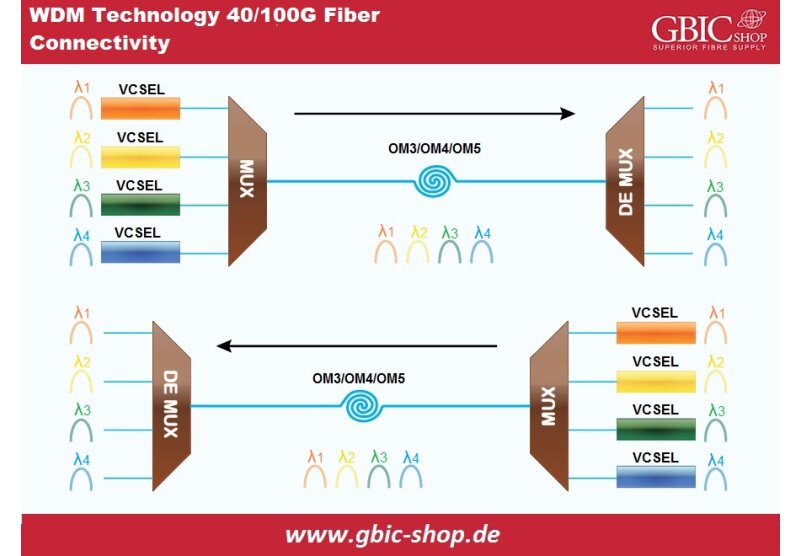
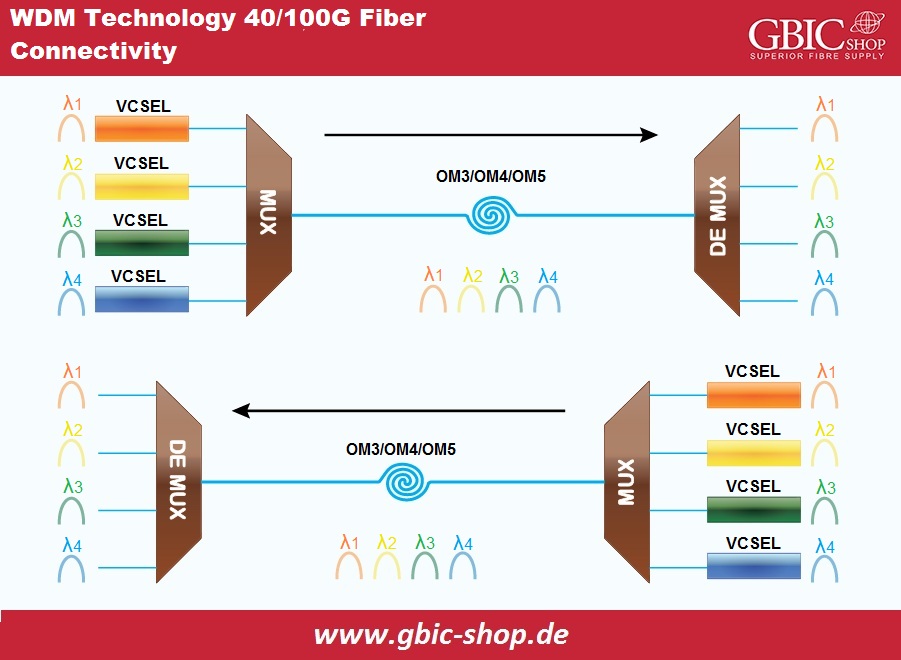
WDM Technology for 40/100G Optical Connections:
With similar fiber optic technologies mentioned earlier, we also have SWDM solutions and BiDi fiber optic modules appropriate for 40/100 Gigabit multi-mode optical fiber applications in data centers. The 40G bi-directional optical transceiver has two 20 Gigabit fiber optic channels for BiDi transmission and reception on each fiber at distances up to 100/150/200m on OM3/OM4/OM5.
The 100 Gigabit bi-directional fiber optic module possesses two 50 Gigabit fiber optic channels and BiDi transmission for each optical fiber. Moreover, the specified range of OM3, OM4, and OM5 can extend to 70,100 and 150m. Furthermore, the SWDM optical module design is primarily for OM3/OM4 optical fiber passage in current data centers reaching 100 Gigabit speed with four fiber optic modules with 25 Gigabit wavelength.
Recommendation for 40/100 Gigabit Multi-mode Optical fiber
A 40/100 Gigabit data center network deployment uses WDM technology or parallel optics with multi-mode optical fiber to provide reliable and cost-effective data transmission. BiDi fiber optic modules and multi-mode optical fiber support 40/100 Gigabit MMF for the deployment of data center networks.
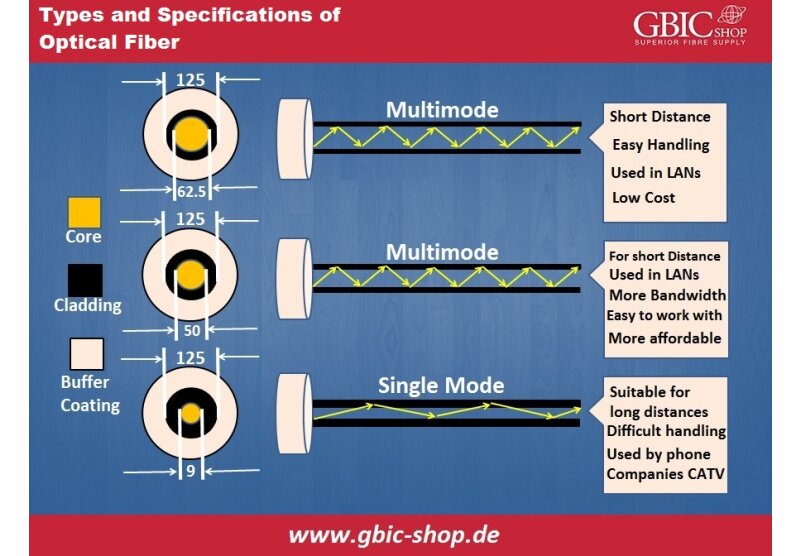
multi-mode optical fiber has less bending or twisting loss than conventional optical cables, making cable maintenance and installation more efficient. It also saves space for high-density cables. OM5 supports new SWDM applications by quadrupling the number of parallel fibers, utilizing only two optical fibers at 40 Gigabits per second and 100 Gigabits per second, and decreasing the fibers' number for excessive speeds.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol