Designing and deploying an optical network solution takes a lot of knowledge of the different types of optical network devices like optical cables, transceivers, cassettes, switches, routers etc. Every little thing should be taken in perspective in order for maximum performance and reliability. One of the key elements are the optical transceivers. They come in many different form-factors and every single of them has its own characteristics and its own place in the network. Knowing the difference between SFP and SFP+, QSFP and QSFP+, CFP, XFP is crucial.
SFP transceivers are Small Form-Factor Transceivers capable to deliver bandwidth up to 2.5 GB/s. They can be used with multi-mode fibers with reach up to 550 meters at 1.25 GB/s or 150 meters in fiber channel at 4.25 GB/s, or with single-mode fibers with reach up to 160 kilometers at 1.25 GB/s.
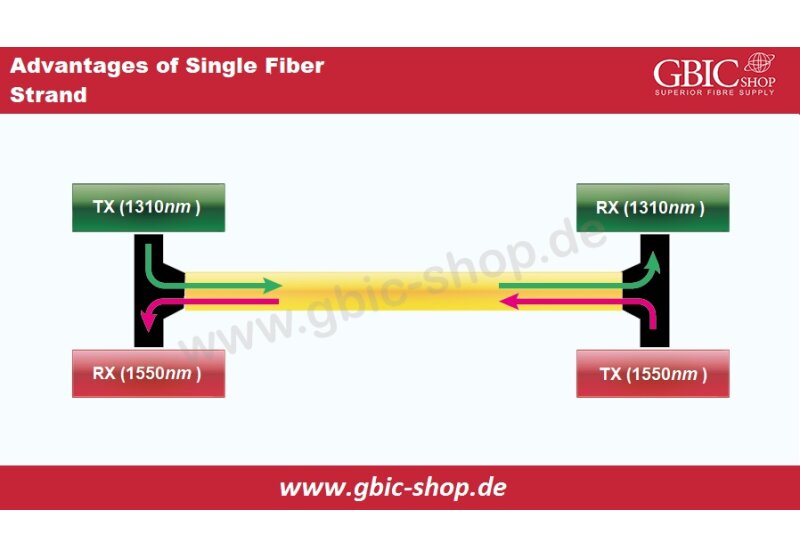
SFP+ transceivers are also Small Form-Factor Transceivers with extended bandwidth support. They can support up to 16 GB/s. SFP+ also introduced the Direct Attach Cables for connecting two SFP+ ports without dedicated transceivers.
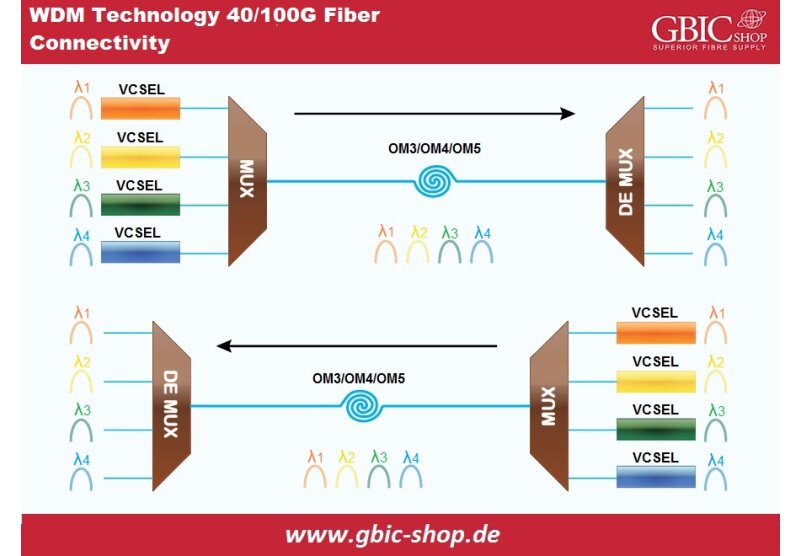
QSFP transceivers are Quad Small Form-Factor Transceivers and they are used for higher bandwidth applications and longer distances. They can also be used for single-mode fibers and multi-mode fibers, however there is a couple of key differences to keep an eye on:
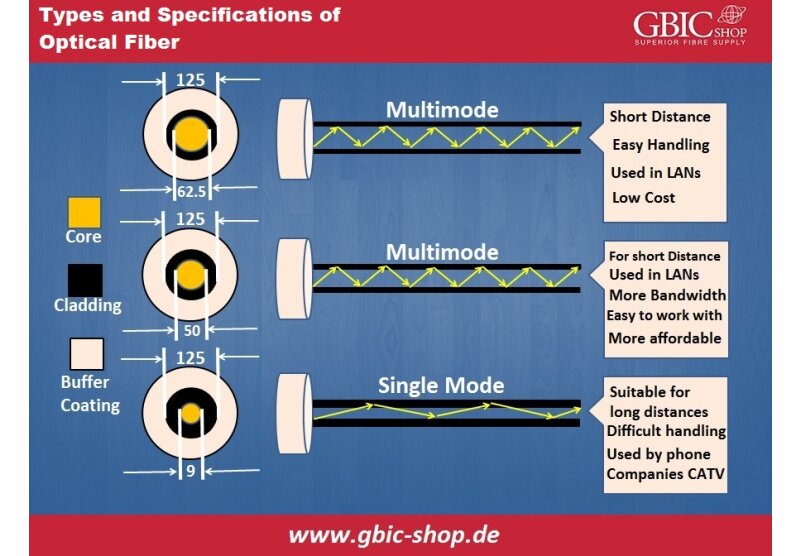
- Singlemode QSFP transceivers have low tolerance for the optics used. Their core is significantly smaller than multi-mode and as a result their wavelength is narrower. With its smaller core and narrower wavelength, the single-mode transceiver has the capability to deliver longer distance and much bigger bandwidth in transmission. These transceivers operate mainly in 1310nm wavelength. There are many types of QSFP single mode transceivers, however generally they can reach up to 40 kilometers. Most commonly they can be found with a duplex LC connector, however there are options for QSFP transceiver with an MPO/MTP connector.
- Multimode QSFP transceivers feature a bigger core and bigger wavelength of optical light. Because their core is significantly bigger compared to single-mode, they can gather much more light from the laser. To put things in perspective, this means that their optics are easier to manufacture and therefore cheaper to purchase. Mainly these transceivers work with 850nm wavelength and are only used for short distances, up to 500 meters. Generally these transceivers use MPO/MTP connectors, however is not uncommon to find a Multi-mode QSFP transceiver with a duplex LC connector.
These differences are important to note when deploying these transceivers in a live network. When choosing whether to choose Multi-mode or Single-mode transceiver we must ensure that both transceivers, at both ends of the connection are the same wavelength and always check twice to be sure. Bending or winding the fiber optic cables connected to them too much would lead to high attenuation (power loss) and performance issues. It is highly advisable that if the transceiver is not used at a given moment, we should always use the dust plug to protect it from dust and other external impacts as this also has a negative impact on its performance. Depending on the distance, ensure you are using the correct Multi-mode fiber (OM3 or OM4) as they provide different ranges. Today the cost plays a huge role in the network infrastructure so we must guarantee a stable and cost-effective network and GBIC-SHOP transceivers are the way to go as they are high quality and fully compatible with over 50 different vendors.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol