Optical transceiver permit the use of fiber to the premises (FTTP) services, in which optical fiber is placed all the way from service provider to the end user location. Placing the fiber all the way to customer end provide internet access at very high-speed. The key benefit of optical technology is its higher data transfer rate.
For using FTTP services, in which fiber is placed all the way to customer premises, the provided fiber optic cable must be terminated into end device. Let that end device be a set top box (STP) from your cable provider to the home users, or any switch, router or any other active device in optical network. As mentioned earlier the active last mile device at customer end, in which fiber is to be terminated, must be equipped with an optical transceiver. An optical transceiver transmits and receives data using optical signal.
There are different types of optical transceivers, proper optical transceiver may be used depending upon application, data rate and services needed. There have been an agreement between different manufactures to produce transceivers that are compatible between different vendors. The agreement is called multi-source agreement (MSA).
Optical transceivers manufactures that follow the multi-source agreement (MSA) include the optical transceivers like SFP, SFP+, XENPAK, QSFP and CFP. MSA strictly direct the operating characteristics of these optical transceivers, which allow MSA compliant optical transceivers to function properly across different vendors.
Following are the details of compatible optical transceivers which are defined by MSA.
SFP

SFP stands for small form-factor pluggable it is a compact hot pluggable transceiver used for both telecom and the data applications. SFP measure 8.5 mm x 13.5 mm x 56.5 mm (H x W x D) in dimensions. Typical SFP modules can be classified based on wavelengths, distance and fiber types used:
For multimode fibers the SFP modules called SX (short reach) module, it use 850 nanometer wavelength. The distance that SX modules support depend on the network speed, for 1.25 gigabit per second speed the distance achieved is about 550 meters, whereas for 125 gigabit per second speed it supports up to 150 meters
For single mode fiber side there are lots of choices, following are the most common types:
For single-mode fibers the SFP modules called LX (long reach) module use 1310 nm for distance up to 10 kilometer. EX module use 1310 nm for distance up to 40 kilometer. ZX module use 1550 nm for distance up to 80 kilometer. EZX module use 1550 nm for distance up to 160 kilometer. CWDM and DWDM SFP transceivers are also used at different wavelengths for reaching several maximum distances. Also there are Gigabit Ethernet UTP copper cable modules available.
SFP+

This is an enhanced version of SFP called SFP+ supports more than 10 gigabit per second and SFP+ is becoming more popular on 10 gigabit ethernet. The enhanced small form-factor pluggable (SFP+) is same the size of SFP, bur it can supports data rate up to 16 gigabit per second.
XENPAK
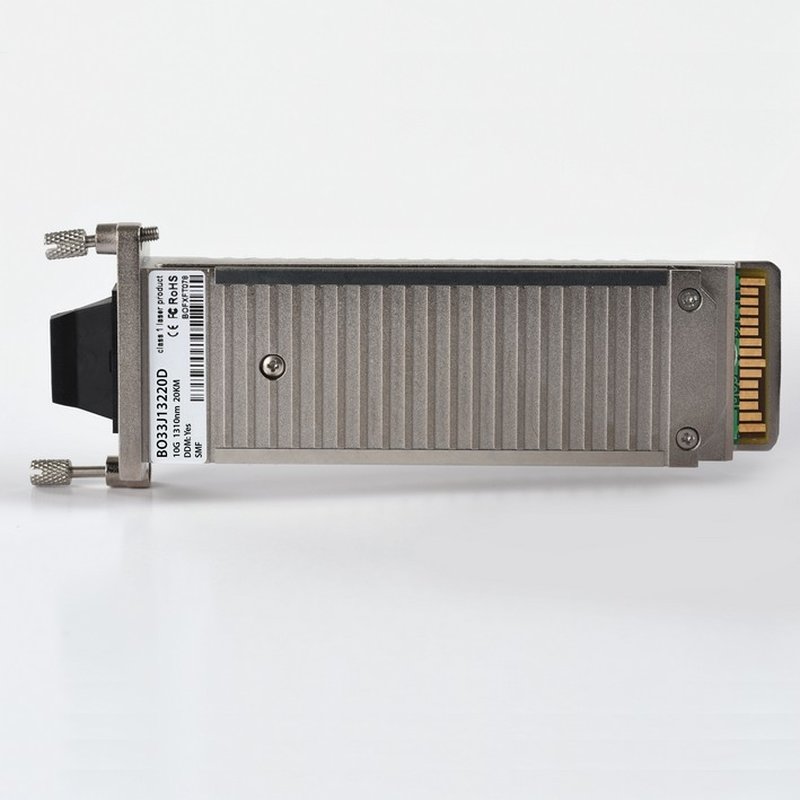

Since XENPAK is also a compatible optical transceiver, multi-source agreement (MSA) that outlines a fiber-optic transceiver module which follows to the 10 Gigabit Ethernet standard. Transmission distances vary from 100 meters to 80 kilometers for fiber. XENPAK has been substituted by more compact optical transceivers, allowing the same functionality. Vendors usually have switched to use SFP/SFP+ modules for greater distances and higher data rates.
QSFP
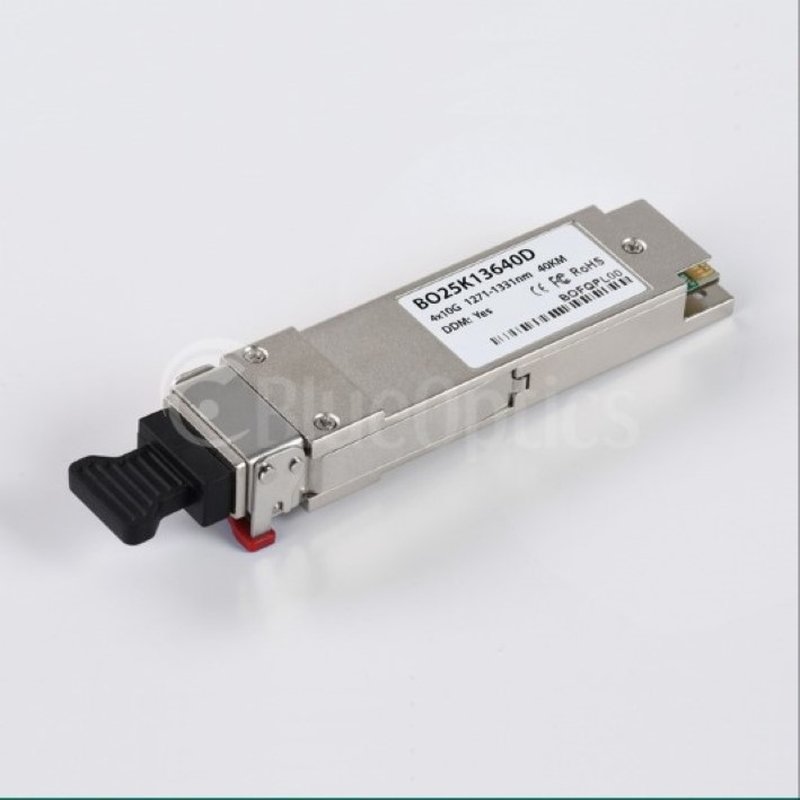

The Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP) is a hot-pluggable and compact optical transceiver used for data communications applications. QSFP measure 8.5 mm x 18.35 mm x 72 mm (H x W x D) in dimensions. QSFP electrical interface and mechanical dimensions are specified by a multi-source agreement (MSA). It is an industry format mutually established and supported by many network component vendors, allowing data rates from 4x10 gigabit per second. The format specification is evolving to enable higher data rates, highest possible rate is 4x28 gigabit per second (also known as QSFP28).
CFP
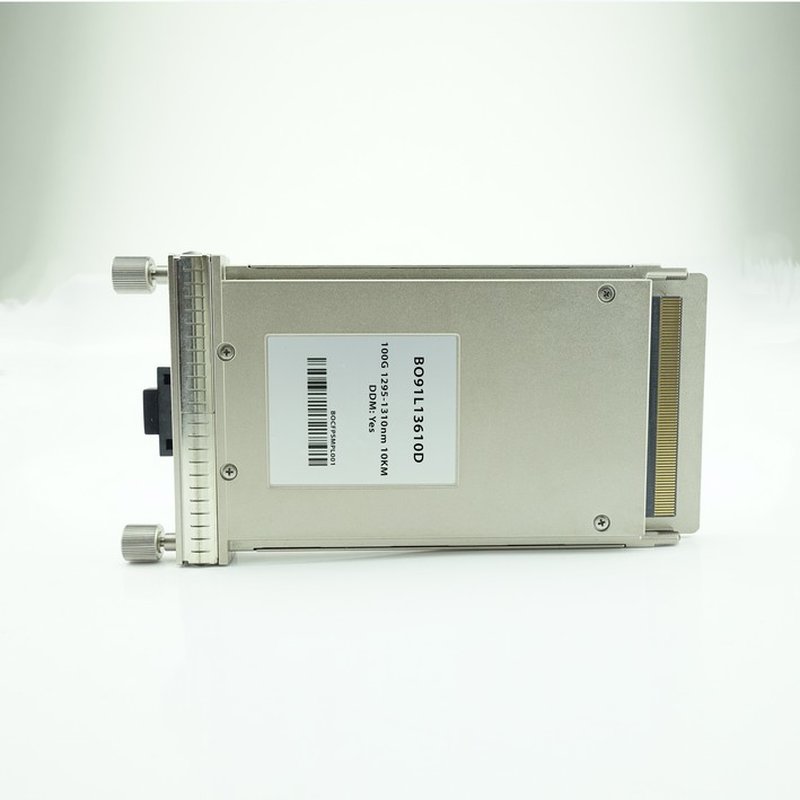

The C form-factor pluggable (CFP) is also a multi-source agreement to produce a common form-factor for the transmission of wider bandwidth digital signals. The C here is taken from Latin letter C used to represent the number 100 (centum), as this standard was mainly established for 100 Gigabit Ethernet. CFP measure 13.6 mm x 82 mm x 145 mm (H x W x D) in dimensions. The CFP-MSA Committee has defined three form factors:
CFP which is currently at standard revision 1.4 and is broadly available in the market, CFP2 which is at draft revision 0.3 is half the size of the CFP transceiver these are recently introduced in the market and CFP4 which is not yet available, is half the size of a CFP2 transceiver, not yet available.
Since these transceivers are specified by a multi-source agreement, which permits compatibility among different vendors. So a single optical transceiver purchased can be used on any vendor.
 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Espaniol
Espaniol