Qualified fiber optic transceivers undergo a sequence of stringent tests before delivery. We consider temperature testing as the most significant part of the testing procedure. How do you determine an optical transceiver's temperature? Why is working temperature essential for a module? What factors affect the working temperature of an optical transceiver? Let's find out answers to these questions.
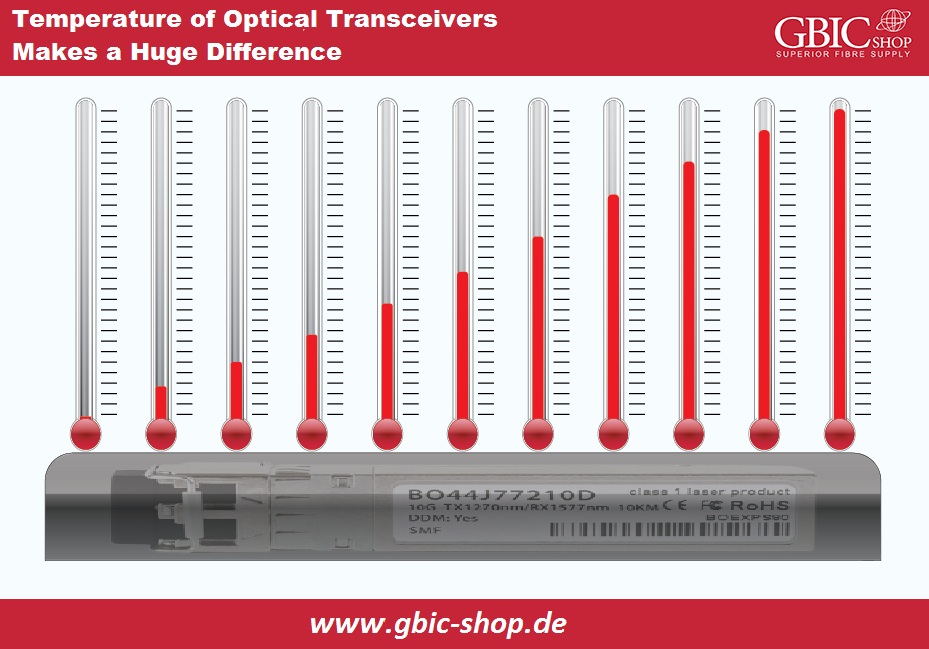
Fundamentals of the Operating Temperature of Fiber Optic Transceivers:
The optical transceiver temperature range determines the digital temperature value of the module we use. Different modules' temperature ratings depend on the type, applications, manufacturers, and form factors. In general, in terms of practical application, we classify the optical transceivers into three temperature standards:
● Commercial Range of Temperature: 0°C to 70°C (labeled “COM”)
● Industrial Range of Temperature: -40°C to 85°C (labeled “IND”)
● Extended Range of Temperature: -20°C to 85°C (labeled “EXT”)
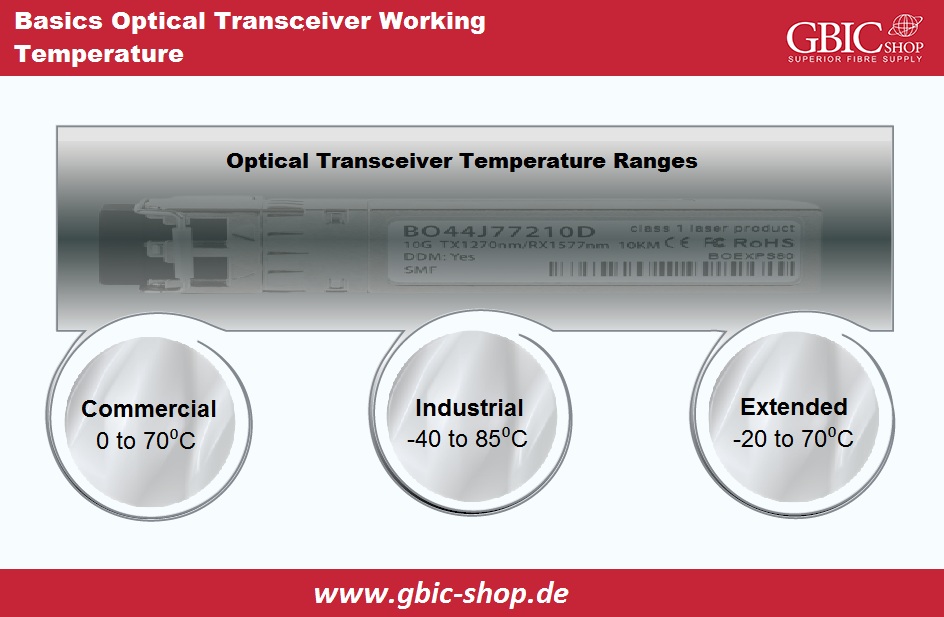
We mainly use optical transceivers in homes, small offices, and large data centers. Nevertheless, we usually deploy the optical transceivers within unpopulated areas like rivers, deserts, mountains, oceans, etc. At the time of purchase, the specification chart determines the module’s temperature range. Depending on the particular application situation, we recommend choosing from the earlier mentioned three temperature ranges.
Importance of the Working Temperature Range of an Optical Transceiver:
Each optical transceiver module has a manufacturer-specified temperature. The module may not work correctly when the temperature is too low or too high, i.e., exceeds or far from the typical temperature range. As a result, we may have the risk of network breakdowns or leading delays.
High-Temperature Challenge:
High temperature leaves an impact on fiber optic communication. Therefore, we have created various techniques to solve the heat problems---putting in a cooling device within data centers and like that. If you think about undertaking deployment in a few extreme conditions, the temperature is a hundred percent non-negligible. If the working temperature is excessive, the module counters a spike within optical power, ensuing in ominous reception signs and disorganized operation, and much worse the module can burn.
Low-Temperature Hazards:
Generally, running a fiber optic system will produce heat. Contrary to the earlier situation, within the data communication industry, there are rare cases where the temperature runs below the temperature the manufacturer specified. If we have a low operating temperature, the performance of the fiber optic transceiver will also become abnormal and unstable. Therefore, in most cases, do not install commercially available fiber optic transceivers in conditions where the temperature is below 0°C.
NOTE: We recommend a temperature control and monitoring system for monitoring in real-time and compensation to ensure that the module has a stable light output and an accurate module extinction rate.
What Affects the Optical Transceivers’ Operating Temperature Range?
Poor Workmanship:
Abnormal transceiver temperatures are ordinary. Modules made from poor quality materials and substandard built-in patterns are susceptible to temperature changes and dissipate heat poorly. Consequently, unstable work is inevitable. We can come out of this difficulty very quickly. Find a reliable supplier with a strict module temperature testing system.
Reusing Used Modules:
Some users consider accepting used modules as "low-priced." The used modules are cost-effective and may work fine in some conditions. However, used transceivers are susceptible to temperature acuteness problems due to their inner components. The most used modules do not reach this level if new modules have a temperature range of 0 to 70°C. If it does not work correctly, maintenance and replacement costs will be higher than the initial savings.
Summary:
It is essential to keep the working temperature of a fiber optic transceiver stable within a value range for daily operation. Optical transceiver vendors increasingly offer different modules depending on their thermal requirements. Each module has undergone rigorous testing, including temperature testing at our test center, to confirm the best performance and quality.
 Espaniol
Espaniol
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English