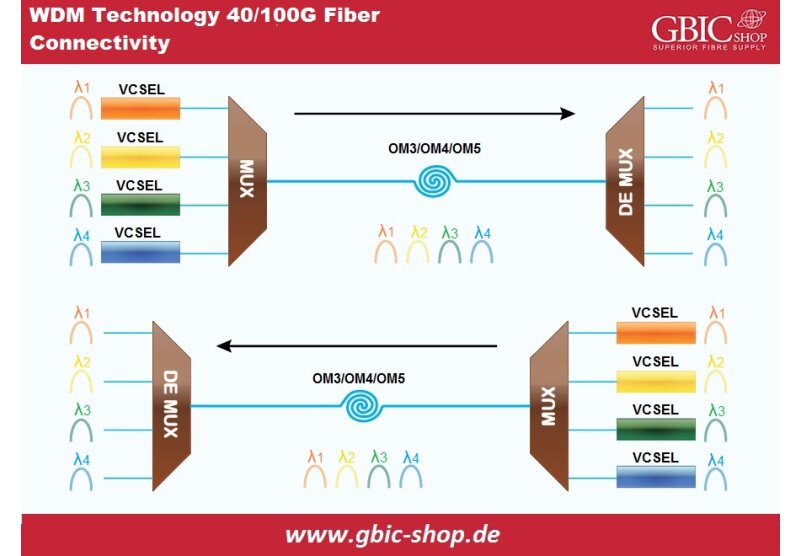
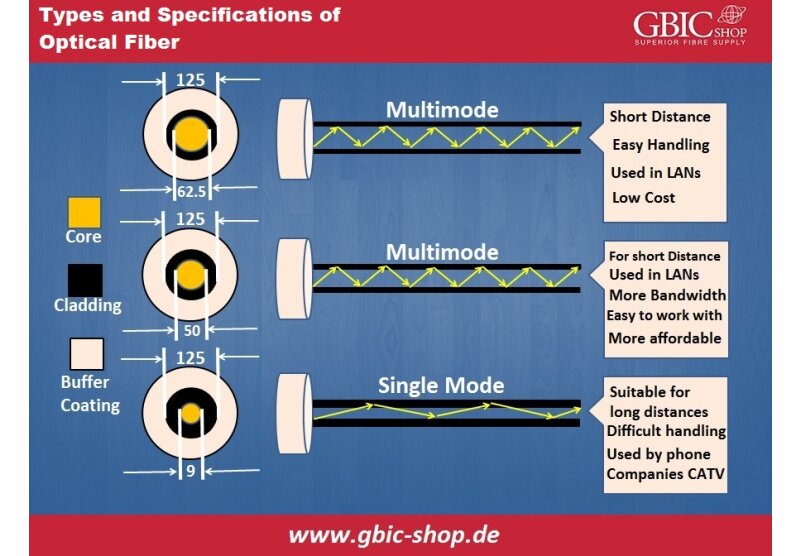
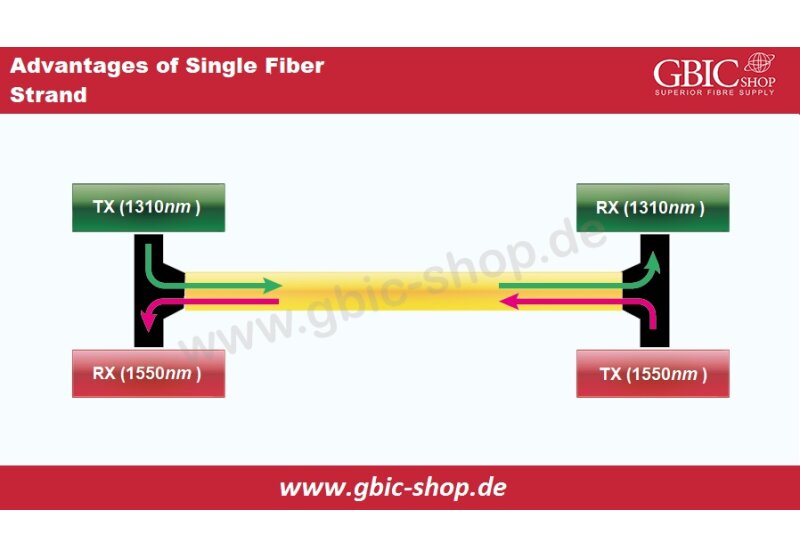
There are several types of cabling that can be used to connect two end points in a communication network. Some of the communication networks use unshielded twisted pair cables (UTP), some use shielded twisted pair cables (STP) and some use the fiber optic cables. It is worth mentioning here that the networking equipment such as switches, routers, computers and servers are all electronic devices and they can only send and transmit electrical signals in the form of bits (0s & 1s). The copper cabling systems such as UTP, STP and co-axial cables are capable of sending and receiving electrical pulses as they are manufactured using conductive materials. The problem with the copper cabling systems is that they are unable to reach longer distances due to the losses that are faced by the electric pulse over the span of the link. To resolve this problem, fiber optic cabling was used. Fiber optic cabling systems can establish reliable communication links over much longer distances as light/laser beams are used to transmit the signal through a tiny glass strand (fiber). As mentioned earlier, the communication equipment is not able to understand the light signal as they are not designed to do so. Research and development experts devised a new method to provide the appropriate interface to the optical fiber cable to the electrical ports of the equipment which was in the shape of SFP transceivers.
The primary application of the SFP transceivers is to connect the optical networks with the electrical interface of the communication equipment. SFP transceivers are modular devices that can be installed and removed in an SFP enabled port on the communication equipment. Figure 1 shows a typical SFP transceiver. This article will discuss the various advantages of using SFP transceivers. These advantages are the basis of the wide acceptance and popularity of SFP transceivers in the field of telecommunication and data networks.
Advantages of SFP Transceivers
Before mentioning the advantages of SFP transceivers, we must have a brief understanding of the predecessor of SFP transceivers, i.e., GBIC transceivers. The GBIC transceiver was developed before SFP transceiver for the very same purpose. The main concern over the GBIC transceiver was the size (form-factor). A GBIC transceiver is almost double the volume of an SFP transceiver. The large size of GBIC transceiver caused it to consume more space in the communication equipment and resulted in low port density per rack-unit. As the fiber optic network grew in size and speeds, the need for higher port density gave birth to the SFP transceivers. SFP transceivers have the following main advantages:
-
Size
- The small size of SFP transceivers provides a very high port density. A normal switch can have as many as 48 SFP ports in a 1 rack-unit form-factor.
- The small size of SFP transceivers provides a very high port density. A normal switch can have as many as 48 SFP ports in a 1 rack-unit form-factor.
-
Compatibility
- The SFP transceivers are manufactured based on the universal standards and guidelines. The cross-platform usage and integration is not a problem when using standards-based SFP transceivers. Furthermore, customers have a choice to use SFP transceivers of any manufacturer with any communication equipment.
- The SFP transceivers are manufactured based on the universal standards and guidelines. The cross-platform usage and integration is not a problem when using standards-based SFP transceivers. Furthermore, customers have a choice to use SFP transceivers of any manufacturer with any communication equipment.
-
Link Speed
- The SFP transceivers can provide 1 Gbps link speed. The design of the SFP transceiver can support up to 5 Gbps throughput.
- The SFP transceivers can provide 1 Gbps link speed. The design of the SFP transceiver can support up to 5 Gbps throughput.
-
Link Distance
- SFP transceivers are most commonly used with fiber optic cables. The link distance that can be achieved over a single-mode fiber optic cable can extend up to 80 kilometers. This is way longer than the 100 meters limit on using the standard copper cabling.
- SFP transceivers are most commonly used with fiber optic cables. The link distance that can be achieved over a single-mode fiber optic cable can extend up to 80 kilometers. This is way longer than the 100 meters limit on using the standard copper cabling.
-
Protocol Independence
- SFP transceivers are passive devices, they do not interfere with the protocol that is being used to transmit and receive the data. This protocol independence makes SFP usable with several applications.
- SFP transceivers are passive devices, they do not interfere with the protocol that is being used to transmit and receive the data. This protocol independence makes SFP usable with several applications.
-
Modular Architecture
- The modular architecture of SFP transceivers enable the network administrators to adopt the pay-as-you-grow model.
- The modular architecture of SFP transceivers enable the network administrators to adopt the pay-as-you-grow model.
-
Hot-Swappability
- SFP transceivers are hot-swappable. They can be installed and removed from an equipment without the need to power-off the equipment. This greatly avoids network outages every time you need to install or remove a transceiver.
The above mentioned advantages of SFP transceivers make them a very popular choice amongst the IT administrators and managers. The advancement in technology and the reduction in the cost of technology have also contributed in the growing usage of SFP transceivers. Although, the 10 Gbps (SFP+), 40 Gbps (QSFP+) and 100 Gbps (CFP) transceivers are also available in the market, the SFP transceivers remain the most extensively deployed transceivers around the world.
 Espaniol
Espaniol
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English