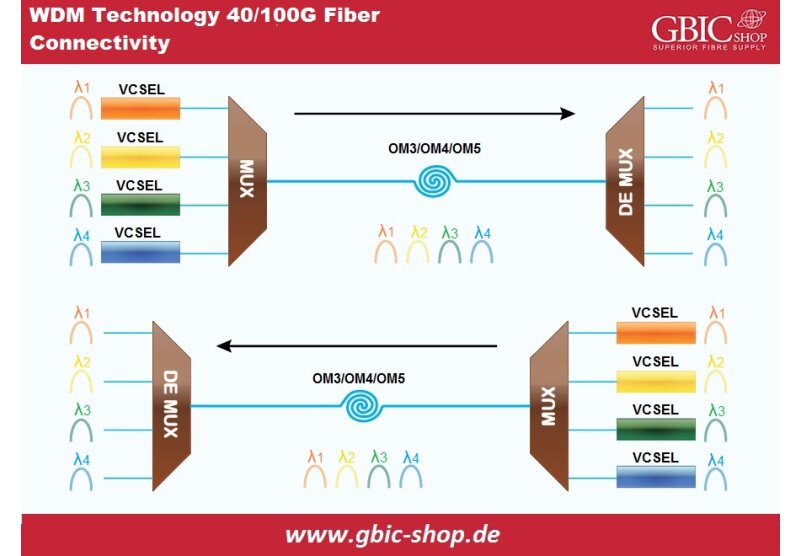
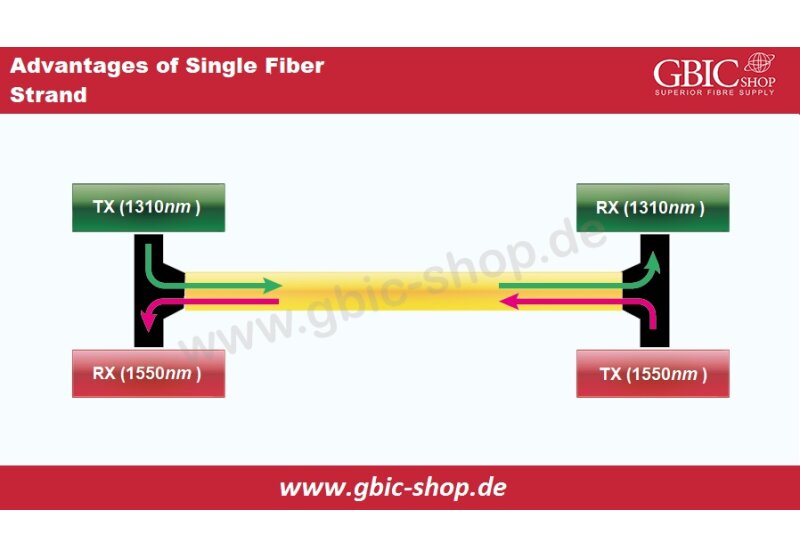
In the 21st century the Datacenters and Service Providers rely on Fiber Optic Networks to provide a stable Internet connection. However, the ever growing business needs and end- customer needs are pushing the networking technology to its limits. The demand for high bandwidth, stable Internet connection, and ready to be a solid ground for future upgrades network, is the main cause for the rapid development of new technologies.
Fiber Optic Networks provides many advantages which guarantee a satisfied IT managers and customers. The whole idea of fiber optic communications is based on two key components: an optical transceiver and an optical fiber cable. These components are the main components that drive the whole fiber network.
The optical transceivers are modules with integrated lasers that transmit the optical light down the cable. However, they are also converting the electrical signal received from the networking device into an optical light. These transceivers are the main engine that drive the optical light to the core of the optical fiber cable. The optical cables are different from the common copper cable. These cables are constructed under a strict supervision, by a high precision machines. They are made of an optical core, the cladding, the coating, strengthening fibers and the jacket. Each of these components has its own function.
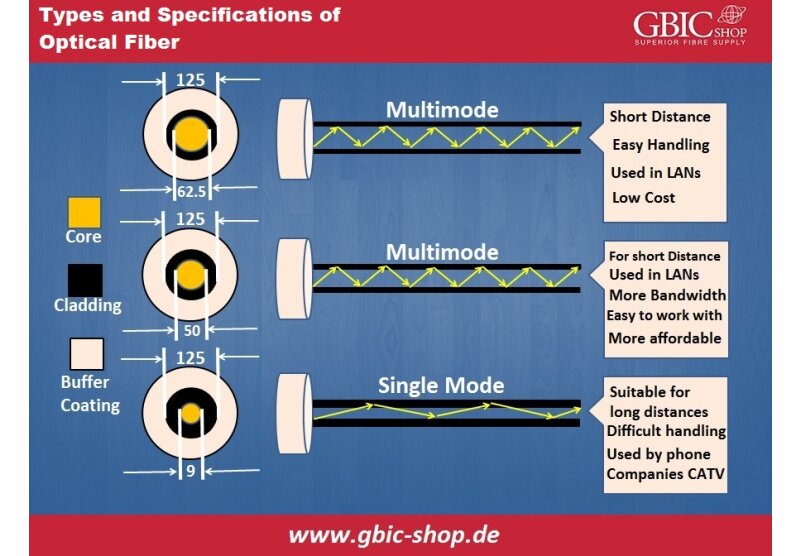
- The core is the physical medium that transports the light. It is made of a single strand, ultra- pure optical glass which is measured in microns by the size of its diameter. Their size depends on the type of the cable, Multi-mode or Single-mode cables. Most common multi-mode core sizes are 50, 62.5 and 100 microns and single-mode cores are generally less than 9 microns.
- The cladding is the thin layer that surrounds the core and it has a shape like a mirror. The cladding helps with the travelling of the data through the cable as the light bounces of off it.
- The coating is a layer of plastic that surrounds the core and the cladding to reinforce the cable and to strengthen its stress durability
- The strengthening fibers are another precautionary measure to help protect the cable from crushing forces and exceeded tension
- The cable jacket is the last layer of the cable which, depending on the manufacturer, can have a different color
Optical fiber cables can be found in two types, Multi-mode and Single-mode fibers. Multi-mode fibers are used for short range connections, depending on the type of the Multi-mode, up to 400 meters. Single-mode fibers are mainly deployed in a long range, high speed connections.
There are many optical transceivers on the market, manufactured by many different vendors. Optical transceivers use the fiber to the premises (FTTP) services, meaning that optical fibers run from the core of the network all the way to the end users. With these services fiber optic networks provide extremely high-speed Internet access. The main advantage of fiber optic networks is the high data transfer rates compared to conventional copper connections.
Two of the most commonly used transceivers are Cisco Systems GLC-SX-MM and GLC-SX-MMD. These are SFP transceivers which support 1000BASE-SX service. They provide 850nm wavelength with dual LC/PC connectors. Even though they are very similar, the key difference that differentiates these two is the extended temperature threshold of the GLC-SX-MMD SFP transceiver. This type of transceivers can operate at temperature range from -5°C to 85°C compared to the GLC-SX-MM type of transceivers which can operate at temperatures from 0 to 70°C. The other difference is the support of the Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM) feature of the GLC-SX-MMD SFP transceiver, compared to the common GLC-SX-MM SFP transceiver. This feature provides a real time monitoring options for monitoring the transmitter and receiver power, the laser bias current, the temperature and the transceiver supply voltage.
With these extended features of the Cisco GLC-SX-MMD SFP transceiver, the maintenance and installation is far easier due to the increased durability of the module itself.
 Espaniol
Espaniol
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English