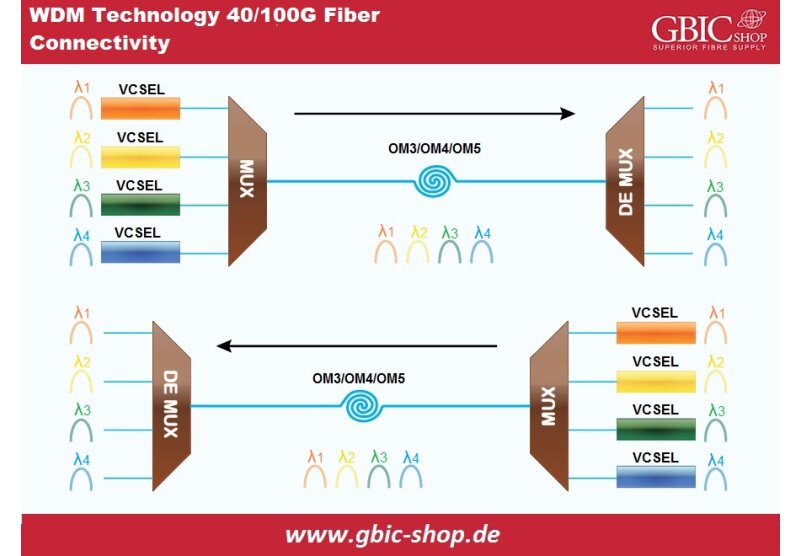
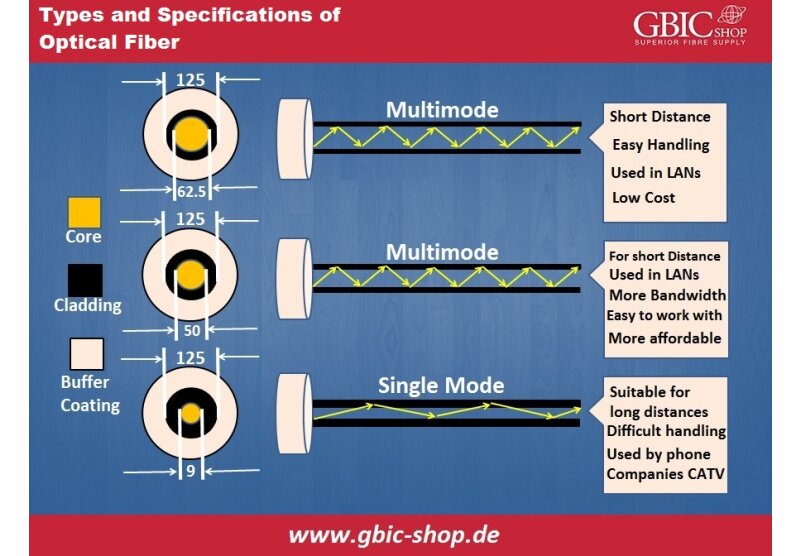
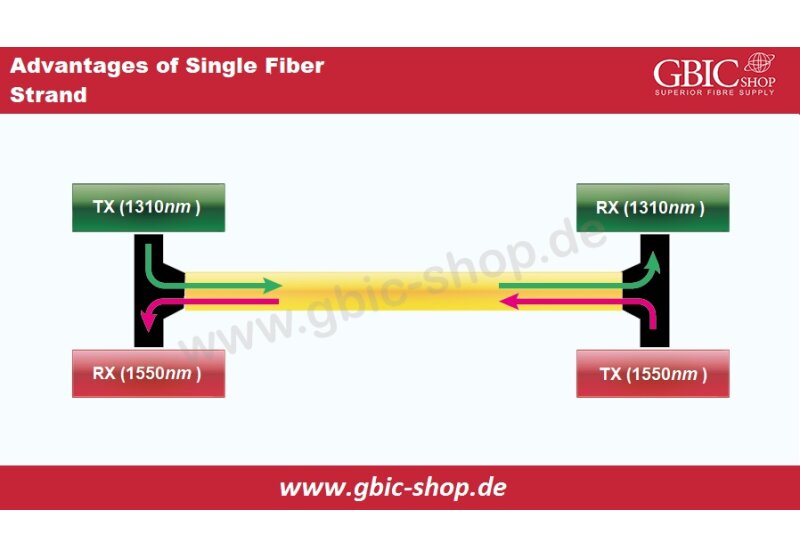
The increasing traffic on the networks has been pushing the limits of the bandwidth of the data centers. Thus the demand for the higher bandwidth was there in the entire run, and to fuel-up the increased demands of the bandwidth and get the scalability in the performance, 400G came into existence. As soon as they came into the market, they got stapled in there and are now known as the hotspot of networking.
The 400G has now been there, and a great focus in the market for a long time, and is serving many or most of the networking vendors. It is the mainstream of the networking industry! The increased usage of 400G, or it being the hotspot, is not there because it was the latest. But, it has been making sense of existing because the requirements were so.
So, there is no doubt that the 400G has been there and will stay there in demand and use for a long time. However, as the requirements of data centers, telecommunication centers, and networking vendors are different, there are different types of form factors of 400G as well, for the different applications. In this article, you will know the different types of applications and a brief introduction about the 400G transceiver types, with their characteristics.
Transceiver Application: Line Side & Client-Side
- Client-Side (PAM4): The client-side interface is like the fiber channels to an end. These transceivers are used for the metro Ethernet, that is, metropolitan-area Ethernet, to the backbone or the core network. This is the transceiver that is best for the small distance transmission in comparison to the line-side. For the network connection, it is required that there should be agreed and a standardized interface. However, PAM4 (4-level pulse amplitude modulation) was selected by the IEEE 802.3bs for 400GE client-side transmission. Now, it was selected because the PAM4 used fewer optical lanes or the lower bandwidth components. As they use the lower bandwidth components, the power consumption and the costs get lower, too, with the denser footprints.
- Line-Side: Now, as compared to the client-side (PAM4), these networks are not used for the metropolitan-area Ethernet. But this is the transceiver that is used for creating networking across thousands of kilometres. Now, they can create the network on just one transceiver connected to fiber for 5 KMs to 10 KMs with the wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). But suppose the connection has to be established for the longer distances. In that case, it requires the connections to be established on the nodes for the transmission, which is the use of sophisticated advanced modulation techniques. With coherent modulation, which is the advanced modulation technique, the establishment of the connections to the longer distances, can be created. This is not only the way to create the connections to the longer distances, but it has a higher data transmission rate and enhanced compensation for optical impairments as well. So, to cover up the requirements of more DSPs and power than in the client-side transmission, many data centers and other networking vendors brought them into use.
The Form Factors: QSFP-DD, OSFP, CFP8
When one has to build the fiber-optic network, there are a lot of things that are added to the checklist to be considered. There are many ways to reach and approach any of the optical communications. So, as there are different ways and devices, all have different usages, pros and cons, and applications too.
In this modern networking, where the traffic is dense and is still increasing day-by-day, the small form-factors are never out of use. Instead, they are the consistent requirement and necessity. So, if there are no such interfaces, then getting the network components that can compete with today’s requirement in this limited space will get complicated and difficult. So, seeing the varied requirements and needs, there are many types of form factors that have emerged with time, having a difference in their application scenarios, the speed that it supports, and more other qualities. So, as there are many form factors of 400G as well, here we will help you get the outline of the three different types of form factors, which are OSFP, QSFP-DD, and CFP8.
OSFP:
- Application: The OSFP is the octal small form factor hot-pluggable network interface used in telecommunication and Data centre’s communication application, supporting the 400G optical data links.
- Size: The size of the OSFP is 22.58mm× 107.8mm× 13mm. These little devices, though, do big work but are very small in size.
- Power Consumption: The power OSFP requires is 15W.
- Is Backward Compatibility With QSFP28 There? The backward compatibility with QSFP28 can be done through an adapter.
- Density Of Switch Port (1RU): The density of the switch port in one rack unit is 36.
- Thermal Management: Thermal management can be done directly.
- Supports 800G? Yes, OSFP can support 800G, as they were made by keeping the 800G in mind.
- Electrical Signalling (Gbps): The electrical signal lines it has are eight, with 50Gbps speed for each lane.
QSFP-DD:
- Application: QSFP-DD is a hot-pluggable network interface used only in the Data centre’s communication application.
- Size: The QSFP-DD is even smaller in size than the OSFP. The size of the QSFP-DD is 18.35mm× 89.4mm× 8.5mm.
- Power Consumption: The total power QSFP-DD would use is 15W.
- Is Backward Compatibility With QSFP28 There? Yes, the backward compatibility with QSFP28 can be done.
- Density Of Switch Port (1RU): The density of the switch port in one rack unit is 36.
- Supports 800G?: No, the QSFP-DD is not capable of supporting 800G.
- Electrical Signalling (Gbps): The electrical signal lines it has are eight, with 50Gbps speed for each lane.
CFP8:
- Application: The CFP8 is also a hot-pluggable network interface, which is though generally and now is only used in telecommunication. But back then, in the year 2015, when they were launched, they were used in the telecommunication and data centers as well.
- Size: As CFP8 is the oldest in them all, the size of the same is bigger than the other two. The size of CFP8 is 40mm× 102mm× 9.5mm.
- Power Consumption: Power consumed done by the CFP8 is 24W.
- Is Backward Compatibility With QSFP28 there? The backward compatibility with QSFP28 cannot be done.
- Density Of Switch Port In One Rack Unit: The density of switch port in one rack unit is 16.
- Supports 800G? The CFP8 does not support 800G.
- Electrical Signalling (Gbps): The electrical signal lines it has are eight, with 50Gbps speed for each lane.
Amongst these three form factors, it can be seen that CFP8 lacks the density and is not compatible with the other two 400G transceivers. If we talk about OSFP, we can clearly see that they are made while keeping in mind the making of 800G. However, coming to QSFP-DD, it has high density, small size, it has the back forward capability that can support QSFP28 as well, which makes the migration of 400G Ethernet easier, and does much more. The QSFP-DD is the one among the three 400G transceivers that withstood the demands of the market of high-density networking. So, seeing these qualities, it can be made out very well that the QSFP-DD form factor is only the one that is appropriate and suitable for the 400g Ethernet applications.
Endnote
There can be many more specifications that can make them compare to each other and describe them in better words. But the mentioned above are the some that are some of the important ones. Alongside, these specifications are enough to say which one of the form factors of 400G was suitable for the 400G Ethernet application. Also, as time has passed and most data centers have the application of QSFP-DD as the 400G transceivers, it is more evidently clear that QSFP-DD is the fittest for the 400G applications.
 Espaniol
Espaniol
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English