Welcome to the fiber optic transceivers benefits: bandwidth, connectivity and long reach data transmission !
GBIC is short for Gigabit Interface Converter, that has been a standard form factor for optical transceivers, commonly used with Gigabit Ethernet and fibre channel in the 2000s.
Optical module was first produced with SC head, as fixed optical transceiver products, usually directly solidified on the circuit board of communication equipment, used as a fixed optical module.
GBIC Fiber Optic Transceivers
GBIC is an input/output transceiver. Its one end is to plug into a Gigabit Ethernet port such as on the switches, and the other end is to connect the fiber optic patch cords and link the fiber optic networks. Therefore, GBIC modules function is to transform the signals between the Ethernet network and fiber optic network.
Applications

GBIC is commonly used with Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel. But its applications are not limited to these two types. There is also Fast Ethernet (FE) GBIC, BIDI GBIC, CWDM GBIC, DWDM GBIC. Generally, GBIC is with the SC connector.
GBIC and SFP are both hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a physical port or a slot. Switches and routers are the main product in a data center that require SFP connectivity at high speeds.
SFP Transceivers

Products began to develop in two aspects: first was towards hot-pluggable feature aspect of the module which become the GBIC and second was towards module miniaturisation with LC head, directly solidified on the board, which SFF modules. When more interfaces were required on the same line card or switch, the big size of GBIC became a problem. Is not feasible due to the size to put a 48 GBIC on a switch so the SFP’s captured all the effort to development although there are equipments that came with line cards that have empty GBIC and SFP slots. If a decision is to be made whenever to equip with GBIC or SFP, it depends on the number of the interfaces required and availability and line cards specific model.
XENPACK Transceivers

The marked continued to ask for high speed, lower power and smaller packages. Xenpack bandwidth was only 2.5 Gb/s due to 8b/10b encoding overhead. Still with four pairs of modules, tha 10 Gb/s could be achieved.
The Xenpack was too expensive and power consumption was high in LAN / SAN environment. Specification was developed by the XFP Multi Source Agreement Group (MSA). It is an informal agreement of an industry group, not officially endorsed by any standards body.
The XFP Transceiver

The great progress in the industry was the miniaturization of the concept appearance of ROSA and TOSA (Receiver and Transceiver Optical Subassemblies). These modules directly modulated the light at 10Gb/s, without the need to combine four 2.5Gb/s lines.Its interface to other electrical components, which is called XFI. XFP modules are hot-swappable and protocol-independent. They typically operate at near-infrared wavelengths (colors) of 850 nm, 1310 nm or 1550 nm.
The SFP+ Transceiver
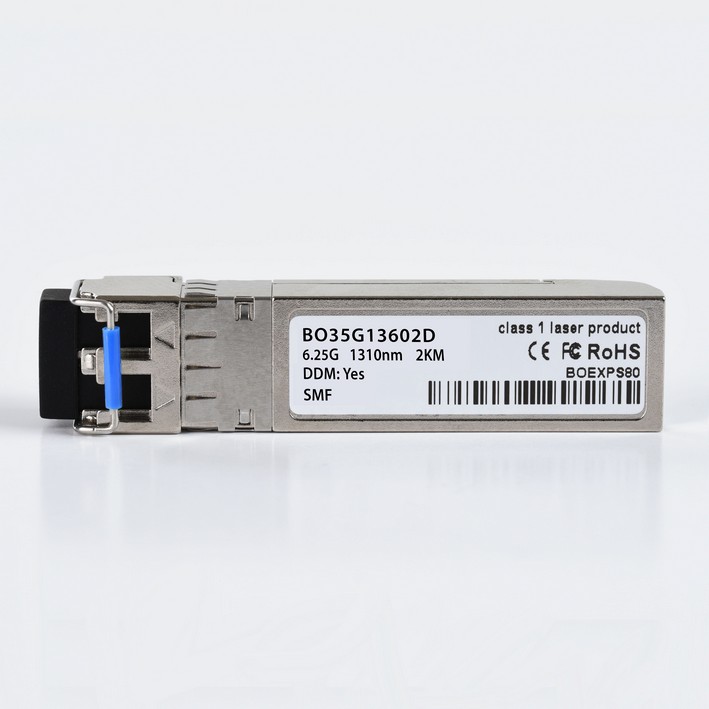

The enhanced small form-factor pluggable (SFP+) is an enhanced version of the SFP that supports data rates up to 16 Gbit/s. 10 Gbit/s SFP+ modules are exactly the same dimensions as regular SFPs, allowing the equipment manufacturer to re-use existing physical designs for 24 and 48-port switches and modular line cards. In comparison to earlier XENPAK or XFP modules, SFP+ modules leave more circuitry to be implemented on the host board instead of inside the module.
The QSFP TRansceiver
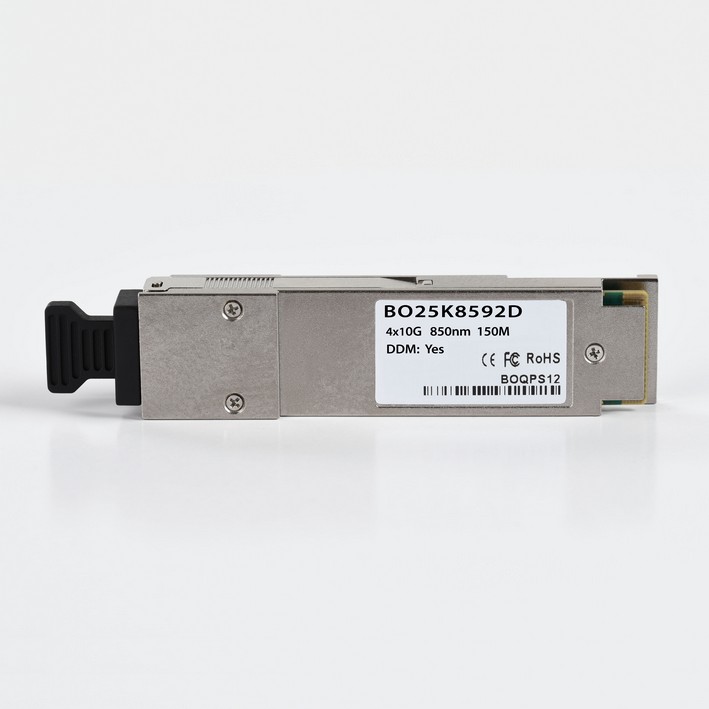

The Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP) is a compact, hot-pluggable transceiver. The form factor and electrical interface are specified by a multi-source agreement (MSA) under the auspices of the Small Form Factor Committee. It interfaces networking hardware (such as servers and switches) to a fiber optic cable or active or passive electrical copper connection. It is an industry format jointly developed and supported by many network component vendors, allowing data rates from 4x1 Gb/s for QSFP and 4x10 Gbit/s for QSFP+ and to the highest rate of 4x28 Gbit/s known as QSFP28 used for 100 Gbit/s links
The CFP Transceiver
The C form-factor pluggable (CFP) is a multi-source agreement to produce a common form-factor for the transmission of high-speed digital signals. The C stands for the Latin letter C used to express the number 100 (centum), since the standard was primarily developed for 100 Gigabit Ethernet systems.
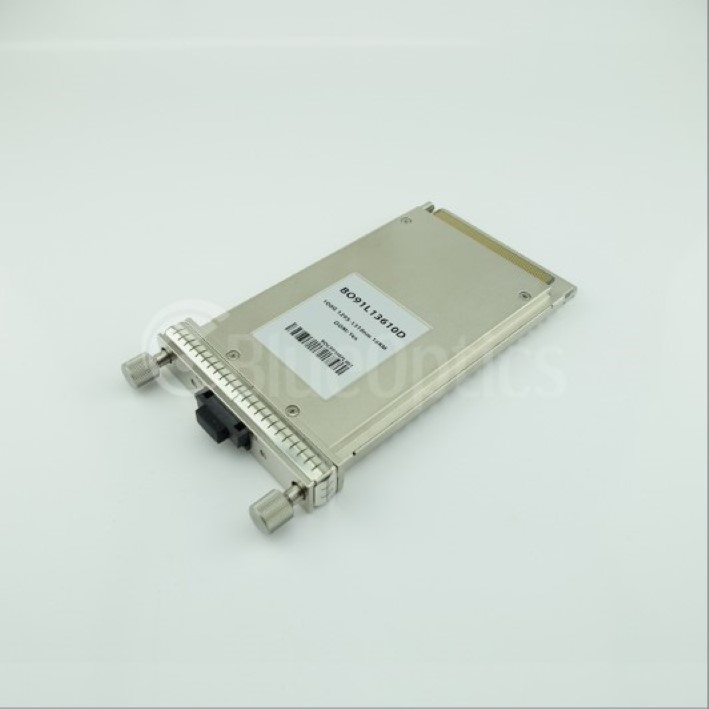

The CFP was designed after the small form-factor pluggable transceiver (SFP) interface, but is significantly larger to support 100 Gbit/s. While the electrical connection of a CFP uses 10 × 10 Gbit/s lanes in each direction (RX, TX), the optical connection can support both 10 × 10 Gbit/s and 4 × 25 Gbit/s variants of 100 Gbit/s interconnects (typically referred to as 100GBASE-SR10 in 100 meter MMF, 100GBASE-LR10 and 100GBASE-LR4 in 10 km SMF reach, and 100GBASE-ER10 and 100GBASE-ER4 in 40 km SMF reach respectively.)
 Espaniol
Espaniol
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English