The fiber wires have replaced the copper wires and other bulky wires, as they are lighter, faster, and more flexible. However, when they are installed, those cables would work very efficiently. But during the installation process, it is indispensable to test the accuracy of the performance to make sure the network integrity stays intact. The loss of signal in the fiber can lead to not so reliable transmission of the data. So, if you very briefly want to know what exactly is fiber loss, and how to calculate the same, read this post, and then you’ll be able to judge the performance of the fiber link.
What Is Fiber Loss?
To provide faster data transmission, fiber cables use light waves to transmit the data. Also, as the fiber optics cables use the light waves for data transmission, the transmission of data is done faster than any other type of cable. Also, these are flexible, lighter, and faster than any other kind of wires. So they have many advantages in the transmission method. However, as these fibers’ performances can’t be neglected, to maintain their performance, there are many things that are required to be taken care of. So, while doing the installation of the fiber optics, it has been one of the primary concerns of the engineers, and cabling designers, that how should they design or installs the cable so that the performance stays upright.
So, now as these cables use the light method to make the signal travel, the distance they travel and the hurdles of the connector and other devices which are there cause to bring down the performance of the fiber cables. So, as the light’s strength gets weaker, and the signal becomes weak, too, this weakening of the light is called fiber optic loss or attenuation. The loss of the light is described in dB.
However, if the fiber cables high-performance is required, and if the signal has to be maintained at par with its given standards, the fiber optic loss has to be reduced. To reduce the fiber loss, knowing the reasons for the same is necessary. Also, it is necessary to calculate the loss so that we can reduce the required amount of loss. Here, before we know how to calculate the loss, we would know the reasons for the attenuation, and then move to the calculation part.
Causes Of Fiber Loss:
The causes of the fiber loss can be said to be sitting on two stations:
- Internal Reason (Intrinsic Fiber Core Attenuation)
Light Absorption - This is one of the most common types of loss of energy in the light. It happens due to internal reasons or because of a structural defect. In this, due to the lights strength being absorbed by the molecular resonance and wavelength and is converted into other kinds of energies, like heat, the strength of the light gets reduced.
Scattering/Dispersion loss - The scattering or the dispersion of the light happens when the light gets dispersed while there are multiple fibers used to make the infrastructure of the cables. So, if the connectors of the extrusion or the coatings of the cables are not designed well, then some light will travel in the straight direction, while some light might get scattered or dispersed. The light that gets scattered or dispersed will be lost and will not be returned. Consequently, that results in the reduction of light and, thus, the signals strength.
- External Reason (Extrinsic Fiber Attenuation)
Bend Loss - The bend loss of the fiber optics is literally real. If the fiber optic is handled not with care, it can lead to the loss of the signal. The bends due to which the loss of the signal causes are of two types, micro bending and macro bending. The macro bending is of 2mm radius. The bending can be because of the fiber deviating from the axis, due to manufacturing defect, mechanical constraints, while fiber laying process can be the other reason, and additional reason can be excess of heat due to environmental change or variations in the environment can be yet another reason for the bend loss.
Fiber Optic Splicing & Connector Loss - Now, fiber optic splicing or the connector loss is the other reason for external fiber attenuation. Connecting two fibers is a task that can’t be avoided, and using the splicing or the connectors both are responsible for the loss in the signal. In which, splicing leads to more loss, but the connector used of high quality will lead to less signal loss.
Standards Of Fiber Optics Attenuation
The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) have developed TIA & EIA standards that specify the transmission rate and performance level of the fiber optic cables, connectors, and other things. The fiber optic loss is defined in the dB/km units, which is one of the most important parameters for fiber loss measurement. Below we will define the cable type wavelength, maximum fiber optic loss, and minimum transmission capacity.
Cable Types:
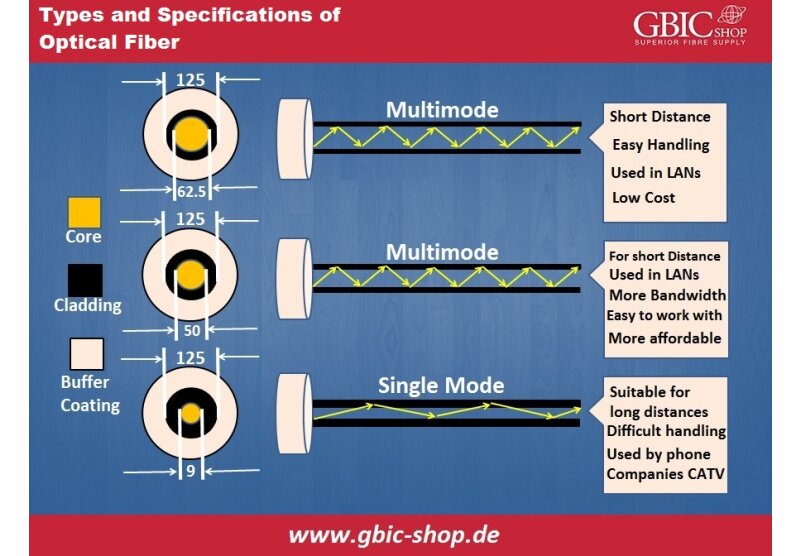
50/125 Micron Multimode
Cable Type Wavelength (nm) - 850/1300
Maximum Attenuation (dB/km) - 3.5/1.5
Minimum Transmission Capacity (Mhz * km) - 500/500
62.5/125 Micron Multimode
Cable Type Wavelength (nm) - 850/1300
Maximum Attenuation (dB/km) - 3.5/1.5
Minimum Transmission Capacity (Mhz * km) - 160/500
Single Mode Inside Plant Cable
Cable Type Wavelength (nm) - 1310/1550
Maximum Attenuation (dB/km) 1.0/1.0
Minimum Transmission Capacity (Mhz * km) - NA/NA
Single Mode Outside Plant Cable
Cable Type Wavelength (nm) - 1310/1550
Maximum Attenuation (dB/km) - 0.5/0.5
Minimum Transmission Capacity (Mhz * km)NA/NA
How To Calculate Optical Fiber Loss?
As we said earlier, to see if the connection of the cable is appropriate or not, it is necessary to calculate the optical fiber loss. So, to calculate, we need the formula only, and the values of fiber optical cable loss vary according to the specification of the manufacturers. So, here we can give you the mantra of calculating the same, that is, formulas, and then you can do the calculation of any given fiber optics installation that is done recently or is being done. So, get the formulas below:
- To Calculate The Total Link Loss: Cable Attenuation + Connector Loss + Splice Loss = Total link loss.
- To Calculate Cable Attenuation (dB): Maximum Cable Attenuation Coefficient (dB/km) × Length in km = Cable attenuation (dB)
- To Calculate Connector Loss (dB): Number of Connector Pairs × Connector Loss Allowance (dB) = Connector loss (dB)
- To Calculate Splice Loss (dB): Number of Splices × Splice Loss Allowance (dB) = Splice loss (dB)
Power Budget Calculation
The fiber optic link budget, also known as loss budget, tells us the amount of optical power loss that is acceptable. However, if the cable plant is not installed correctly, and if there is much loss of the link, then the budget might exceed, which will lead to the loss, and the plant will not be maintained well.
So, here we can give you the formula to calculate the power budget (PB).
To Calculate PB, the result of differences between the sensitivity of the receiver, which is called PR, and with the output of the transmitter into the fiber, which is called PT.
The Calculating Formula: PB = PT - PR. Explicitly, suppose if the average transmitter output power is - 20dBm, and the receiver sensitivity is -26dBm, then the power budget will be -14dBm - (-26dBm) = 12dBm
Power Margin Calculation
After calculating the link loss and the power budget, you can also calculate the power margin, which is also called the safety margin. The power margin represents the power amount that is available after subtracting link loss from that of the power budget.
The Formula To Calculate Power Margin: PM = PB - LL.
Endnote
So, if you have read this entire post, you must have a complete idea about what is fiber loss, what are its types, and so you can also judge how to reduce the loss as well. Moreover, with the introduction to the fiber loss, we have also provided the formulas on how to calculate the losses so that you can know if the installation done at the place is best or not. If you are getting the new fiber optics installation done, make sure you do all these calculations.
 Espaniol
Espaniol
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 English
English